The Classification Standard of 304 Stainless Steel Smart Lock
304 stainless steel is one of the commonly used stainless steel grades, prized for its balance of corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and cost-effectiveness. It consists primarily of iron, with chromium (typically 18%) and nickel (about 8%) to enhance corrosion resistance and strength.
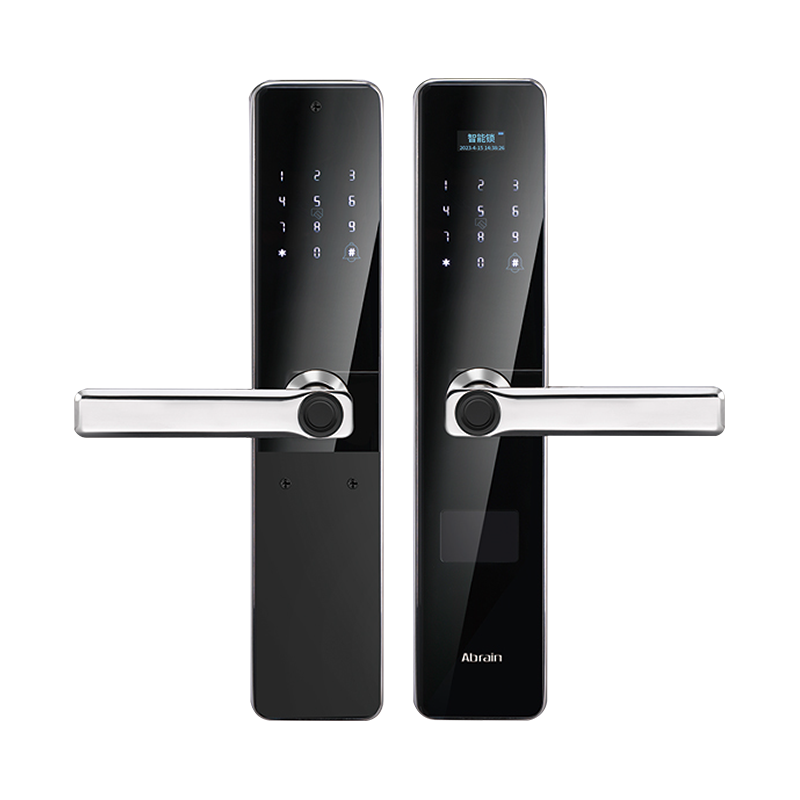

In smart locks, 304 stainless steel is preferred for components exposed to external environments, such as lock bodies, handles, and faceplates. The material resists rust and deterioration caused by moisture, humidity, and varying weather conditions, which helps extend the lock's service life.
Classification by Material Quality
The classification standard of 304 stainless steel smart locks begins with material quality verification. This classification ensures that the steel used complies with international standards such as ASTM A240 or equivalent, which specify the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing methods.
Key quality indicators include:
Chemical Composition: The content of chromium, nickel, carbon, manganese, and other trace elements must be within prescribed limits to guarantee corrosion resistance and mechanical strength.
Mechanical Properties: Tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation percentage must meet defined thresholds to ensure durability.
Surface Finish: The stainless steel should have a smooth, polished finish to prevent micro-cracks or surface defects that could compromise corrosion resistance.
Manufacturers often provide certification or test reports to confirm the 304 stainless steel grade used in smart locks.
Functional Classification of Smart Locks
Beyond material quality, 304 stainless steel smart locks are classified by their functional characteristics, which include locking mechanisms, unlocking methods, and additional features. Common classifications include:
Mechanical vs. Electronic: Some locks combine mechanical keys with electronic control for dual access, while others are fully electronic with no physical key option.
Unlocking Modes: Smart locks may support biometric (fingerprint), keypad codes, RFID cards, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or a combination of these.
Installation Type: Locks are classified as mortise, cylindrical, or deadbolt, depending on their fitting and use cases.
Power Supply: Battery-powered, rechargeable, or wired locks have different operational considerations and classifications.
Each functional classification impacts the lock's application, installation process, and user experience.
Security Level Classification
Security is a critical aspect of smart locks. For 304 stainless steel smart locks, classification standards include security ratings that assess resistance to forced entry, tampering, and environmental factors.
Standards such as ANSI/BHMA (American National Standards Institute/Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association) grading or EN 14846 (European standard for locks) provide a framework for security classification. Locks are rated based on:
Force Resistance: Ability to withstand physical attacks like drilling, prying, and impact.
Locking Mechanism Complexity: The sophistication of internal mechanisms, such as anti-pick pins or deadbolt throw length.
Electronic Security: Encryption strength for wireless communication, biometric accuracy, and protection against hacking.
304 stainless steel contributes to the mechanical strength portion of these evaluations by providing a sturdy, corrosion-resistant body less susceptible to damage.
Environmental and Durability Standards
Given that many smart locks are installed on exterior doors, environmental resilience is part of their classification. Standards such as IP (Ingress Protection) ratings assess how well the lock resists dust, water, and other environmental hazards.
304 stainless steel locks typically meet or exceed IP54 or IP65 standards, indicating protection against dust ingress and water spray or jets, respectively. This classification confirms the lock's suitability for outdoor use, especially in humid or rainy climates.
Durability tests may also include temperature cycling, UV resistance for plastic or coated parts, and wear tests on moving components.
Quality Control and Testing
Classification standards for 304 stainless steel smart locks emphasize rigorous quality control throughout manufacturing and post-production. Testing protocols include:
Material Testing: Verification of steel grade through spectrometry and mechanical tests.
Functional Testing: Assessment of unlocking methods, battery life, response time, and firmware reliability.
Security Testing: Simulated break-in attempts and electronic security evaluations.
Environmental Testing: Exposure to moisture, dust, temperature changes, and mechanical wear.
Only products that meet or exceed these standards qualify as certified 304 stainless steel smart locks, providing confidence to end-users and installers.