Understanding the Classification of Waterproof Smart Locks
One of the common classifications of the Waterproof Smart Lock factory is by its unlocking mechanism. Some models use fingerprint recognition, allowing authorized users to gain access through biometric identification. Others utilize PIN codes, RFID cards, Bluetooth signals, or mobile app commands. Each method offers a different balance of convenience, speed, and user management capability. For instance, a Waterproof Smart Lock that operates via a mobile app may support remote access and activity tracking, while one that relies on a fingerprint sensor may prioritize personal access without network connectivity.
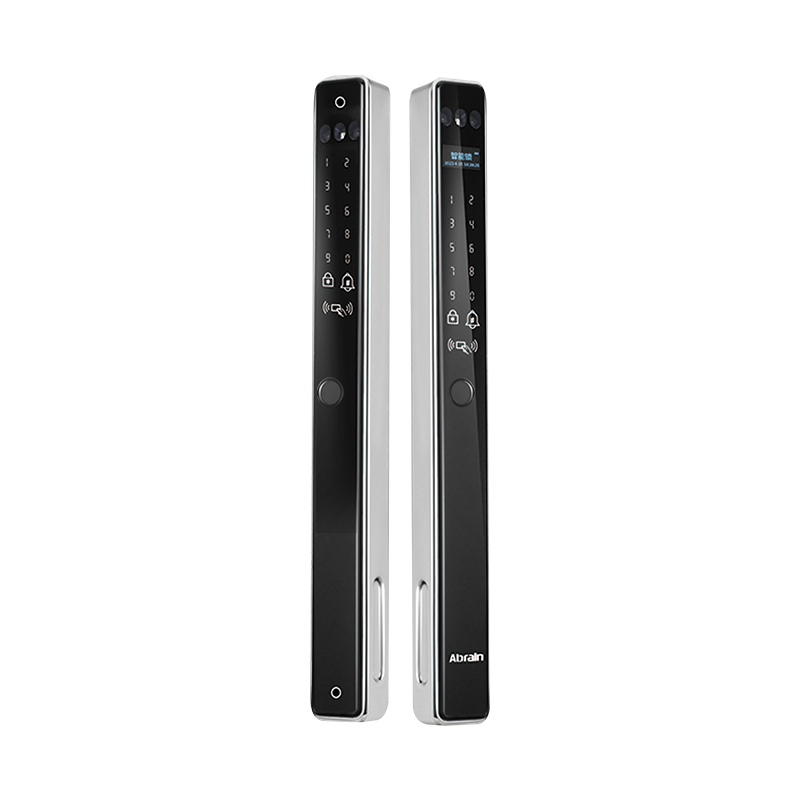

Another classification system focuses on power options. The majority of Waterproof Smart Lock models are battery-powered, using either disposable or rechargeable batteries. This allows for flexible installation, especially in areas where electrical wiring is not feasible. Some advanced versions incorporate solar charging features or low-power standby modes to extend operational time. Battery-powered Waterproof Smart Lock units typically include power indicators and low-battery alerts to maintain uninterrupted access.
A third way to categorize the Waterproof Smart Lock is by its usage environment. While all models are designed to withstand moisture, some are built for outdoor use, such as gates, storage units, or waterfront properties. These are rated with high ingress protection (IP) levels, commonly IP65 or higher, to resist dust and water intrusion. Others may be more suitable for semi-covered areas, such as apartment balconies or carports, where occasional splashes or humidity are concerns but direct exposure is limited. The environmental rating of a Waterproof Smart Lock is an important factor in selecting the appropriate model for a specific location.
Installation method also plays a role in classifying the Waterproof Smart Lock. Surface-mounted models are designed for straightforward attachment to existing doors or panels, often with minimal modification. Mortise-style locks, on the other hand, are recessed into the door and may require professional installation. The decision between these types depends on the structure of the door and the level of integration desired. Some Waterproof Smart Lock systems come as part of a full lockset, while others are designed as retrofit devices to upgrade traditional locking systems.
Material construction is another factor that contributes to classification. A Waterproof Smart Lock intended for marine environments may include stainless steel or coated metal components that resist corrosion from saltwater. Other models may be constructed with durable plastic casings and rubberized buttons to ensure long-term reliability in rain or snow. Regardless of the material, the outer shell of a Waterproof Smart Lock is engineered to protect the internal circuit boards and locking mechanisms.
From a technological standpoint, some Waterproof Smart Lock devices are equipped with advanced features such as audit trails, automatic locking, and integration with home automation platforms. These functions can be included in both consumer and commercial-grade models. In large facilities, administrators might use a central system to control multiple Waterproof Smart Lock units across various entry points.
User management is another angle from which to evaluate the classification of the Waterproof Smart Lock. Some models are designed for single-user operation, while others support dozens or even hundreds of individual profiles. This makes them suitable for shared access scenarios, such as in coworking spaces or short-term rental properties, where access needs to be updated frequently and remotely.